Smart OJ判题系统
复习一下项目开发流程
- 项目简介、项目调研、项目需求分析
- 核心业务流程
- 项目功能模块
- 技术选型
- 项目初始化
- 项目开发
- 测试
- 优化
(代码提交、代码审核、产品验收) - 上线
在此过程中,也是要不断写文档、持续调研、沉淀知识的
项目简介
OJ : Online Judge(在线判题评测系统)
用户可以选择题目练习,在线编写代码,测试代码,提交代码,系统会根据设置好的答案对用户提交的代码进行评测,给出评测结果!
项目亮点
- 项目新颖,重复度低,写简历有区分度
- 区别于常见的
CRUD项目,偏向于架构设计、编程思想之类的知识 - 项目复杂度高,可扩展性强
OJ系统的常用概念
ac 表示你的题目通过,结果正确
题目限制:时间限制、内存限制
题目介绍
题目输入
题目输出
题目输入用例
题目输出用例
难点:判题系统
普通测评:
管理员设置题目的输入和输出用例,比如我输入 A,你要输出 B 才是正确的;交给判题机去执行用户的代码,给用户的代码喂输入用例,比如 A,看用户程序的执行结果是否和标准答案的输出一致。
(比对用例文件)
特殊测评(SPJ):
管理员设置题目的输入和输出,比如我输入 1,用户的答案只要是 > 0 或 < 2 都是正确的;特判程序,不是通过对比用例文件是否一致这种死板的程序来检验,而是要专门根据这道题目写一个特殊的判断程序,程序接收题目的输入(1)、标准输出用例(2)、用户的结果(1.5) ,特判程序根据这些值来比较是否正确。
交互测评:
让用户输入一个例子,就给一个输出结果,交互比较灵活,没办法通过简单的、死板的输入输出文件来搞定
不能让用户随便引入包、随便遍历、暴力破解,需要使用正确的算法。 => 安全性
判题过程是异步的 => 异步化
提交之后,会生成一个提交记录,有运行的结果以及运行信息(时间限制、内存限制)
项目调研
https://github.com/HimitZH/HOJ(适合学习)
https://github.com/QingdaoU/OnlineJudge(python,不好学,很成熟)
https://github.com/hzxie/Noj(星星没那么多,没那么成熟,但相对好学)
https://github.com/vfleaking/uoj(php实现的)
项目需求分析
实现核心
- 权限校验
- 代码沙箱(安全沙箱 – 防止代码藏毒)
代码安全:设置安全的、隔离的沙箱,以确保用户的代码不会影响到系统的安全 - 判题规则
题目用例的比对,结果的验证 - 任务调度
资源分配:防止用户疯狂占用资源,措施:异步化处理,服务资源有限,按照用户提交顺序进行判题
核心业务流程

时序图:

功能
- 题目模块
a. 管理员:创建、删除、修改
b. 用户:搜索题目
c. 在线做题、提交题目代码 - 用户模块
a. 注册与登录 - 判题模块
a. 提交判题(结果是否正确与错误)
b. 错误处理(内存溢出、安全性、超时)
c. 自主实现代码沙箱(安全、隔离的一个环境)
d. 开放接口
扩展思路
- 支持多种语言
- 远程评测
- 完善的评测功能:普通评测、特殊评测、交互评测、在线自测、文件IO
- 统计分析判题记录
- 权限校验
技术选型
前端:
Vue3、手撸Umi项目模板、AcroDesign组件库、在线代码编辑器、在线文档浏览
后端:
Java进程控制、Java安全管理、部分JVM知识点、虚拟机、Docker、Spring Cloud微服务、消息队列
架构设计
采用分层架构:用户层、接入层、业务层、服务层、存储层、资源层

项目排期
- 项目简介、项目调研、需求分析、技术选型、架构设计、现有
OJ主流实现方案 - 前后端项目初始化、前端通用项目模板的搭建
- 主业务流程的前后端开发(争取把代码沙箱之外的全部搞定)
- 专攻代码沙箱(自主实现,不止一种实现方案,层层递进,通过实战用例来进行安全优化)
- 系统优化(微服务改造、系统扩展思路)
主流OJ实现方案
- 用现成的
OJ系统
网上有很多开源的OJ项目,比如青岛OJ、HustOJ等,可以直接下载开源代码自己部署。
比较推荐的是judge0,这是一个非常成熟的商业OJ项目,支持 60 多种编程语言!
代码:https://github.com/judge0/judge0
- 用现成的服务
如果你不希望完整部署一套大而全的代码,只是想复用他人已经实现的、最复杂的判题逻辑,那么可以直接使用现成的 判题API、或者现成的 代码沙箱 等服务。
比如judge0提供的判题API,非常方便易用。只需要通过 HTTP 调用submissions判题接口,把用户的代码、输入值、预期的执行结果作为请求参数发送给judge0的服务器,它就能自动帮你编译执行程序,并且返回程序的运行结果。
API的作用:接受代码、返回执行结果
Judge0 API地址:https://rapidapi.com/judge0-official/api/judge0-ce
官方文档:https://ce.judge0.com/#submissions-submission-post
流程
1先注册
2再开通订阅
3然后测试 language 接口
4测试执行代码接口 submissions
- 自主开发✨✨✨–我的方案
自主实现判题服务和代码沙箱,适合学习,但不适用于商业项目。
- 把 AI 来当做代码沙箱
现在 AI 的能力已经十分强大了,我们可以把各种本来很复杂的功能直接交给 AI 来实现。
只要脑洞够大,AI + 编程 = 无限的可能~
- 移花接木
这种方式最有意思、也最 “缺德”。很多同学估计想不到。
那就是可以通过让程序来操作模拟浏览器的方式,用别人已经开发好的 OJ 系统来帮咱们判题。
比如使用 Puppeteer + 无头浏览器,把咱们系统用户提交的代码,像人一样输入到别人的 OJ 网页中,让程序点击提交按钮,并且等别人的 OJ 系统返回判题结果后,再把这个结果返回给我们自己的用户。
这种方式的缺点就是把核心流程交给了别人,如果别人服务挂了,你的服务也就挂了;而且别人 OJ 系统不支持的题目,可能你也支持不了。
后端项目初始化
五步走:
- 选中项目全局搜索替换springboot-init为新项目名
- 选中包,全局更改替换包名springbootinit
- 更改包名
- 本地新建数据库,直接执行sql/create table.sql脚本,修改库名为yuoj,执行即可
- 改application.yml配置,修改MySQL数据库的连接库名、账号密码,端口号
初始化模板待完善的地方:
- 日志:根据错误类型分类,分级归档
- 扩展:引入分布式锁、多线程、线程池
项目模板复习
1)先阅读README.md
2)sql/create table.sql定义了数据库的初始化建库建表语句
3)sql/post_es mapping,json帖子表在ES中的建表语句
4)aop:用于全局权限校验、全局日志记录
5)common:万用的类,比如通用响应类
6)config:用于接收application.yml中的参数,初始化一些客户端的配置类(比如对象存储客户端)
7)constant:定义常量
8)controller:接受请求
9)esdao:类似mybatis的mapper,用于操作ES
10)exception:异常处理相关
11)job:任务相关(定时任务、单次任务)
12)manager:服务层(一般是定义一些公用的服务、对接第三方APl等)
13)mapper:mybatis的数据访问层,用于操作数据库
14)model:数据模型、实体类、包装类、枚举值
15)service:服务层,用于编写业务逻辑
16)utils:工具类,各种各样公用的方法
17)wxmp:公众号相关的包
18)test:单元测试
19)MainApplication:项目启动入口
20)Dockerfile:用于构建Docker镜像
基本开发流程
库表设计
- 根据功能设计库表
- 用户表
字段:id、账号、密码、昵称、头像、简介、用户角色、微信开放平台id、公众号openId、创建时间、修改时间、是否删除(项目全局配置文件中已经配置了 MybatisPlus isDelete 字段为逻辑删除)
2. 题目表
字段:
题目相关:id、标题、内容、标签、答案、提交数量、通过数量、通关率(扩展);
判题相关:判题用例(judgeCase / json)、判题限制(judgeConfig / json)、判题类型(扩展);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| [
{
"input": "1 2",
"output": "3 4"
},
{
"input": "1 3",
"output": "2 4"
}
]
|
1
2
3
4
5
| {
"timeLimit": 1000,
"memoryLimit": 1000,
"stackLimit": 1000
}
|
3. 用户-题目提交表
字段:用户id、题目id、语言、代码、判题状态、判题信息(judgeInfo / json);
1
2
3
4
5
| {
"message": "{$ 判题信息枚举值 $}",
"time": 1000,
"memory": 1000
}
|
枚举值信息:
- ACCEPT 通过
- WRONG_ANSWER 答案错误
- COMPILE_ERROR 编译错误
- MEMORY_LIMIT_EXCEEDED 内存溢出
- TIME_LIMIT_EXCEETED 超时
- PRESENTATION_ERROR 展示错误
- OUTPUT_LIMIT_EXCEEDED 输出溢出
- WAITING 等待中
- DANGEROUS_OPERATION 危险操作
- RUNTIME_ERROR 运行错误
- SYSTEM_ERROR 系统错误
数据库表字段存 json 的前提:
首先,字段含义相关,属于同一类;
其次,不需要根据 json 中的某一字段进行查询;
最后,字段存储不用占用太多空间。
存 json 的好处:
便于扩展,即:不用修改库表结构,就可以直接操作对象内部的字段
小知识(数据库索引):
什么时候适合加索引?如何给某个字段加上索引?
首先,索引需要建立在有区分度的字段上;
其次,需要从我们的实际业务出发,无论是单个索引,还是联合索引,都需要从实际的查询语句、字段枚举值的区分度、字段的类型考虑,特别是 where 条件指定的字段。
例如:where userId = 1 and questionId = 2,这个时候就可以分别建立索引,或者是联合索引,如果是数据量不大的话,尽量不用索引,因为索引也需要占用空间。(待考证!!!)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| # 数据库初始化
# @author <a href="https://github.com/wl2o2o">程序员CSGUIDER</a>
# @from <a href="https://wl2o2o.github.io">CSGUIDER博客</a>
create database if not exists smartoj;
use smartoj;
CREATE TABLE if not exists user (
id bigint auto_increment comment 'id' primary key,
userAccount varchar(256) not null comment '用户账号',
userPassword varchar(512) not null comment '用户密码',
userName varchar(256) null comment '用户昵称',
userAvatar varchar(1024) null comment '用户头像',
userProfile varchar(512) null comment '用户简介',
userRole varchar(256) default 'user' not null comment '用户角色',
unionId varchar(256) null comment '微信开放平台id',
mpOpenId varchar(256) null comment '微信公众号id',
createTime datetime default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP not null comment '创建时间',
updateTime datetime default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP not null on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP comment '更新时间',
isDelete tinyint default 0 not null comment '逻辑删除',
index idx_unionId (unionId)
) comment '用户表' collate = utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
# 字段:
# 题目相关:id、标题、内容、标签、答案、提交数量、通过数量、通关率(扩展);
# 判题相关:判题用例(judgeCase / json)、判题限制(judgeConfig / json)、判题类型(扩展);
CREATE TABLE if not exists question (
id bigint auto_increment comment '题目id' primary key,
userId bigint not null comment '创建用户id',
title varchar(256) not null comment '题目标题',
tags varchar(256) not null comment '题目标签',
content text not null comment '题目内容',
answer text null comment '题目答案',
judgeCase text not null comment '判题用例',
judgeConfig text null comment '判题限制',
submitNum int default 0 null comment '提交数量',
acceptNum int default 0 null comment '通过数量',
thumbNum int default 0 null comment '点赞数量',
favourNum int default 0 null comment '收藏数量',
createTime datetime default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP not null comment '创建时间',
updateTime datetime default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP not null on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP comment '更新时间',
isDelete tinyint default 0 not null comment '逻辑删除',
index idx_userId (userId)
) comment '题目表' collate = utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
# 字段:用户id、题目id、语言、代码、判题状态、判题信息(judgeInfo / json);
CREATE TABLE if not exists question_submit (
id bigint auto_increment comment 'id' primary key,
userId bigint not null comment '创建用户 id',
questionId bigint not null comment '题目 id',
language varchar(128) not null comment '编程语言',
code text not null comment '用户代码',
status int default 0 not null comment '判题状态(0 - 待判题、1 - 判题中、2 - 成功、3 - 失败)',
judgeInfo text null comment '判题信息(json 对象)',
createTime datetime default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP not null comment '创建时间',
updateTime datetime default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP not null on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP comment '更新时间',
isDelete tinyint default 0 not null comment '是否删除',
index idx_questionId (questionId),
index idx_userId (userId)
) comment '题目提交表' collate = utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
|
代码生成方法
- 使用 MyBatisX 插件,会自动根据库表字段,一键生成业务的基础 CRUD 代码
- 编写 Controller 层代码(根据模板进行复用,复制逻辑相同代码,替换字段)
- 编写 DTO、VO、枚举值字段,用于接受前端请求或者业务间传递信息。(复用项目模板)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| package com.yupi.yuoj.model.enums;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.ObjectUtils;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public enum QuestionSubmitLanguageEnum {
JAVA("java", "java"),
CPLUSPLUS("c++", "c++"),
GOLANG("golang", "golang");
private final String text;
private final String value;
QuestionSubmitLanguageEnum(String text, String value) {
this.text = text;
this.value = value;
}
public static List<String> getValues() {
return Arrays.stream(values()).map(item -> item.value).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public static QuestionSubmitLanguageEnum getEnumByValue(String value) {
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(value)) {
return null;
}
for (QuestionSubmitLanguageEnum anEnum : QuestionSubmitLanguageEnum.values()) {
if (anEnum.value.equals(value)) {
return anEnum;
}
}
return null;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public String getText() {
return text;
}
}
|
- 编写一些独立的类,因为以上库表中设计的含有 JSON 字段,为了方便处理 JSON 中的某个字段。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
@Data
public class JudgeCase {
private String input;
private String output;
}
|
- 校验 Controller 类,解决报错
- 编写 Service 代码,完成业务逻辑
小知识:
为什么要加上业务前缀(上述代码中的JudgeCase),什么时候不加?
首先,增加业务前缀有利于增加区分度,防止多表中重复类名产生冲突;
其次,通常情况下,我们希望抽出一个公用类来共享,这时不需加业务前缀。
什么是 VO 类?有什么用?
VO:View Object(显示层对象)—— 专门给前端返回、显示的对象,一般会过滤脱敏掉一些不需要返回给前端的字段,保证安全性,不仅更加方便展示给用户,而且方便展示给前端开发者,还可以节约网络传输大小。
DTO:Data Transfer Object(数据传输对象)
BO:Bussiness Object(业务对象)
怎么防止爬虫爬取题目?有什么简单的方法?
建议把题目的 id 生成规则 改为 ASSIGN_ID ,这样就可以通过其底层的雪花算法:ASSIGN_UUID 随机生成一个 32 位的 id,有效避免爬虫对题目的爬取。
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
|
@TableId(type = IdType.ASSIGN_ID)
private Long id;
|
查询提交信息接口(网站的提交信息实时监控面板)
- 功能:
- 根据用户 ID 查询
- 题目 ID 查询
- 编程语言查询
- 题目状态查询
- 注意事项:
- 实现方案:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @Override
public QuestionSubmitVO getQuestionSubmitVO(QuestionSubmit questionSubmit, User loginUser) {
QuestionSubmitVO questionSubmitVO = QuestionSubmitVO.objToVo(questionSubmit);
long userId = loginUser.getId();
if (userId != questionSubmit.getUserId() && !userService.isAdmin(loginUser)) {
questionSubmitVO.setCode(null);
}
return questionSubmitVO;
}
|
todo: 熟悉快速 CRUD 的步骤,过项目模板,充分理解;完善更加通用的 Controller、Service 代码。
判题机模块架构设计
这就是架构师的工作:先跑通完整的业务流程,在进行代码沙箱复杂的实现
判题模块与代码沙箱的关系
判题模块:
调用代码沙箱,把代码和输入用例交给代码沙箱去执行
代码沙箱:
接收代码和输入用例,返回编译运行的结果,不负责判题(可以作为独立的项目或者服务,提供给其他需要执行代码的项目去使用)
架构图:
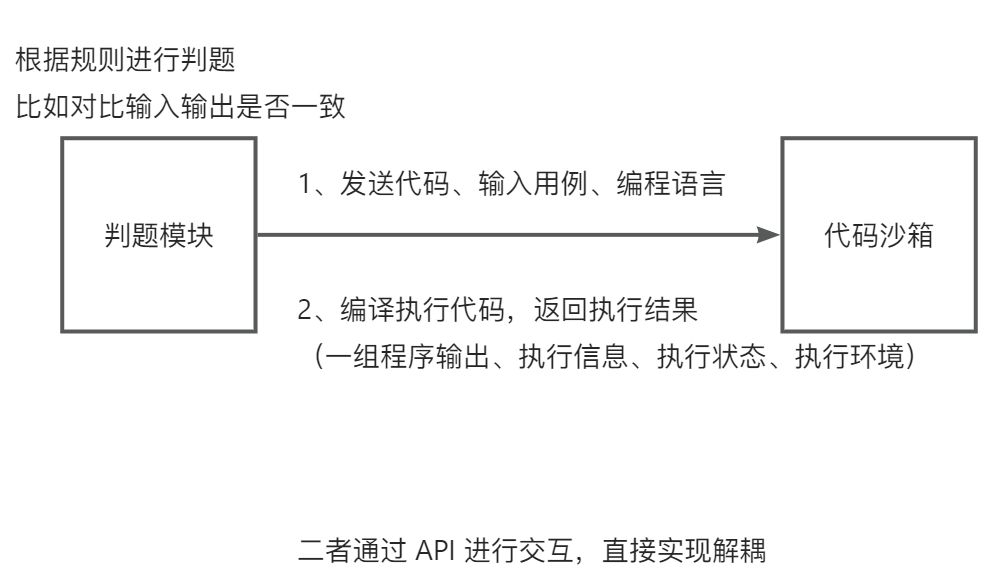
思考:
为什么要直接执行一组输入用例和输出一组运行结果?
试想,如果是对于每一个用例都要执行调用一次 代码沙箱 API 接口的话,需要多次的网络传输、程序需要多次的编译、记录程序的执行状态。造成的资源浪费严重。
这样就是骆驼驮运货物是分多次还是一次性过河!
这是一种很常见的性能优化的方法:批处理!
代码沙箱架构开发
为了提高代码沙箱的通用性(便于后期进行扩展 AI 判题或者远程判题),
我们定义代码沙箱为接口,这样就便于后期进行扩展了⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
- 定义代码沙箱为接口,提高通用性
这样,我们之后的项目判题模块代码只调用代码沙箱的接口进行判题,不用调用实现类,
这样就可以不用更改代码了(之更改调用的接口)
TODO: 代码沙箱的请求接口中,判题的 timeLimit 可以不加,也或者自行扩展(扩展点)
扩展思路:增加一个代码沙箱状态的接口
- 定义所种不通风的代码沙箱的实现
示例代码沙箱——打通流程
远程代码沙箱——调用实际的接口
第三方代码沙箱——调用网上现成的代码沙箱(例如:goJudge——https://github.com/criyle/go-judge)
- 编写单元测试,验证单个代码沙箱的执行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| @SpringBootTest
class CodeSandboxTest {
@Test
void executeCode() {
CodeSandbox codeSandbox = new RemoteCodeSandbox();
String code = "int main() { }";
String language = QuestionSubmitLanguageEnum.JAVA.getValue();
List<String> inputList = Arrays.asList("1 2", "3 4");
ExecuteCodeRequest executeCodeRequest = ExecuteCodeRequest.builder()
.code(code)
.language(language)
.inputList(inputList)
.build();
ExecuteCodeResponse executeCodeResponse = codeSandbox.executeCode(executeCodeRequest);
Assertions.assertNotNull(executeCodeResponse);
}
}
|
目前还存在一个问题,就是我们的测试中把代码沙箱的选择已经写死了,如果项目后面需要改为其他沙箱,那么就需要改动很多代码。所以。。。。。。
我们可以使用工厂模式来解决这个难题。
- 使用工厂模式,直接根据用户在配置文件中传入的字符串参数(指定的沙箱类别),来生成对应的代码沙箱实现类
此处,我们使用的是静态工厂模式,实现比较简单,符合需求
示例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public class CodeSandboxFactory {
public static CodeSandbox newInstance(String type) {
switch (type) {
case "example":
return new ExampleCodeSandbox();
case "remote":
return new RemoteCodeSandbox();
case "thirdParty":
return new ThirdPartyCodeSandbox();
default:
return new ExampleCodeSandbox();
}
}
}
|
扩展思路:
如果确定代码沙箱中不会出现线程安全问题,你什么可以使用单例工厂模式。
详细见聚合搜索项目。
使用工厂模式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
String type = scanner.next();
CodeSandbox codeSandbox = CodeSandboxFactory.newInstance(type);
String code = "int main() { }";
String language = QuestionSubmitLanguageEnum.JAVA.getValue();
List<String> inputList = Arrays.asList("1 2", "3 4");
ExecuteCodeRequest executeCodeRequest = ExecuteCodeRequest.builder()
.code(code)
.language(language)
.inputList(inputList)
.build();
ExecuteCodeResponse executeCodeResponse = codeSandbox.executeCode(executeCodeRequest);
}
}
|
- 参数配置化:
在application.yml中进行配置指定代码沙箱的变量:
1
2
3
|
codesandbox:
type: example
|
在 Spring 的 Bean 中通过**@Value**注解来使用配置文件中的代码沙箱:
1
2
| @Value("${codesandbox.type:example}")
private String type;
|
- 代码能力增强
比如,我们需要调用代码沙箱前后输出参数日志,输出响应结果日志,便于管理员进行分析。
那么我们需要在每一个类中都写上log.info吗?
代理模式:
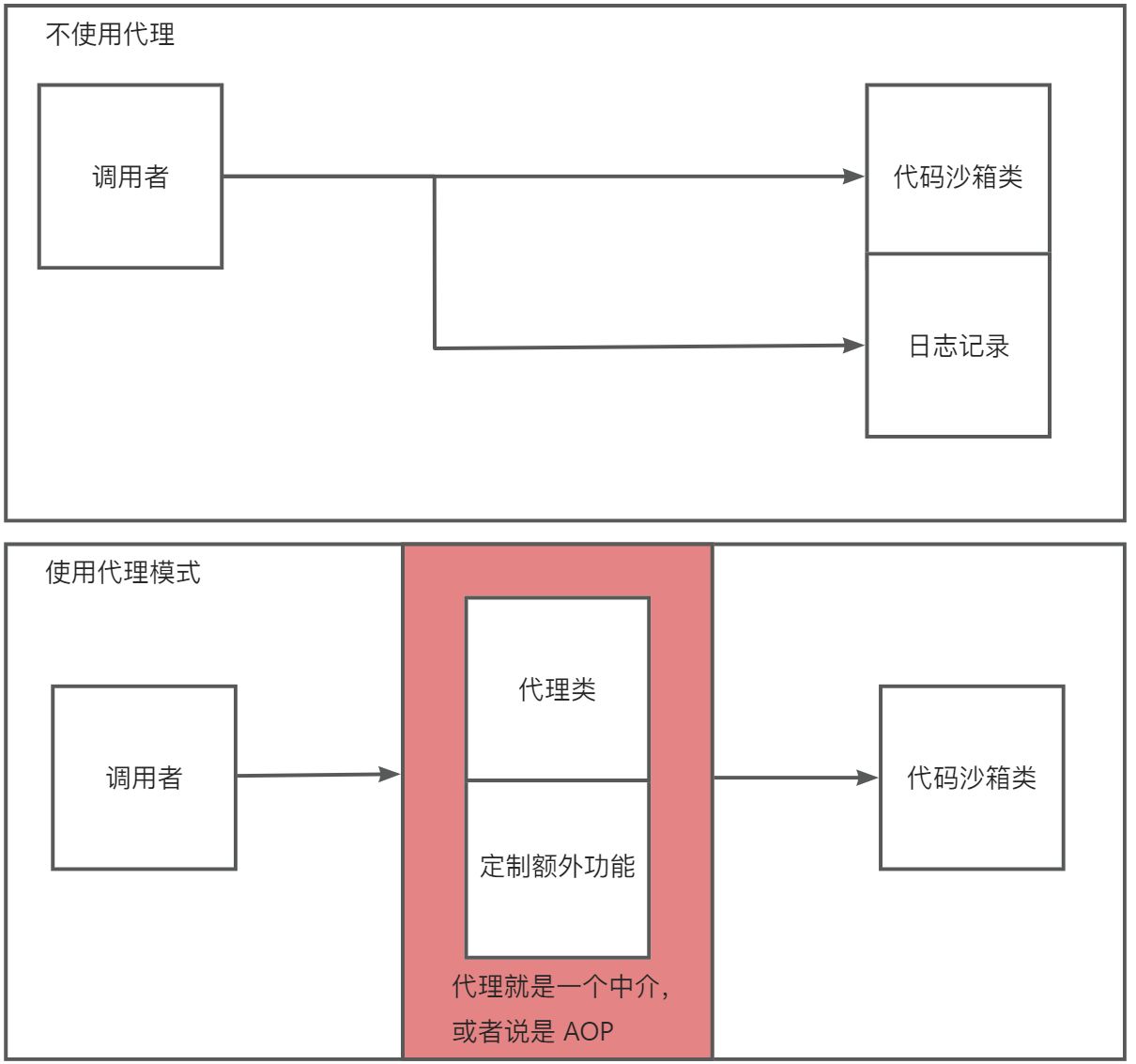
代理模式的实现原理:
- 实现被代理的接口
- 通过构造函数接受一个被代理的接口实现类
- 通过被代理的接口实现类,增加代理需要实现的操作
示例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| @Slf4j
public class CodeSandboxProxy implements CodeSandbox {
private final CodeSandbox codeSandbox;
public CodeSandboxProxy(CodeSandbox codeSandbox) {
this.codeSandbox = codeSandbox;
}
@Override
public ExecuteCodeResponse executeCode(ExecuteCodeRequest executeCodeRequest) {
log.info("代码沙箱请求信息:" + executeCodeRequest.toString());
ExecuteCodeResponse executeCodeResponse = codeSandbox.executeCode(executeCodeRequest);
log.info("代码沙箱响应信息:" + executeCodeResponse.toString());
return executeCodeResponse;
}
}
|
使用方式:
1
2
| CodeSandbox codeSandbox = CodeSandboxFactory.newInstance(type);
codeSandbox = new CodeSandboxProxy(codeSandbox);
|
- 实现示例代码沙箱
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
@Slf4j
public class ExampleCodeSandbox implements CodeSandbox {
@Override
public ExecuteCodeResponse executeCode(ExecuteCodeRequest executeCodeRequest) {
List<String> inputList = executeCodeRequest.getInputList();
ExecuteCodeResponse executeCodeResponse = new ExecuteCodeResponse();
executeCodeResponse.setOutputList(inputList);
executeCodeResponse.setMessage("测试执行成功");
executeCodeResponse.setStatus(QuestionSubmitStatusEnum.SUCCEED.getValue());
JudgeInfo judgeInfo = new JudgeInfo();
judgeInfo.setMessage(JudgeInfoMessageEnum.ACCEPTED.getText());
judgeInfo.setMemory(100L);
judgeInfo.setTime(100L);
executeCodeResponse.setJudgeInfo(judgeInfo);
return executeCodeResponse;
}
}
|
知识点 - LomBok Buider 注解:
我们通常创建一个对象之后都是通过 set、get 进行存取值的,其实还有一种更为便捷的 set 值的方式:builder
使用方法:
- 实体类加上
@Builder注解 - 链式地给对象进行赋值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| @Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Animals {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
}
Animals dog = Animals.builder()
.id(1)
.name("翠花")
.age(18)
.builder();
|
TODO 完成示例代码沙箱 —> 改为远程代码沙箱
判题服务完整业务流程开发
判题服务业务流程:
- 传入题目的 id ,获取到对应的题目、提交信息(包含代码、编程语言等)
- 调用沙箱,获取执行结果
- 根据执行结果,判断 –> 设置题目判题状态与信息
以上是最基本的判题业务流程,但是还不够完整,存在点击多次、多次判题的 Bug,那么就要给判题设置一个状态了!
完善后的判题服务业务流程:
- 传入题目的 id ,获取到对应的题目、提交信息(包含代码、编程语言等)
- if (判题状态不为等待中) 抛出异常;
- 更改判题状态为判题中
- 调用沙箱,获取执行结果
- 根据代码沙箱执行结果,判断运行结果是否则正确 –> 设置题目最终的判题状态与信息
判断逻辑:
- 先判断,代码沙箱执行的结果输出数量是否和预期输出数量是否一致
- 依次判断每一项的预期输出是否相等
- 判题题目的限制是否符合要求
- 其他异常
注意:
如果我们的代码沙箱执行程序需要十秒钟,这个时间可能根据编程语言的不同而该变动,那么怎么解决?
A:我们可以采取策略模式,针对不同的情况,定义不同的策略,以便于进行修改与维护。这样就可以改善业务代码中**if else**成堆,业务逻辑不清晰的情况。
如何实现策略模式?
- 定义判题上下文对象,用于定义在策略中传递的参数(可以理解为DTO)
- 定义策略接口,让代码更加通用化
- 实现默认的业务策略(剪切
judgeService中判题逻辑的相关代码) - 针对不同语言实际情况,定义不同的策略
切换策略时,难免会使用if else,考虑到降低耦合度,我们可以将切换策略的逻辑抽离出来,单独编写一个判断切换策略的类
- 编写一个判断切换策略的类
StrategyManage
示例代码:
- 定义判题上下文对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| @Data
public class JudgeContext {
private JudgeInfo judgeInfo;
private List<String> inputList;
private List<String> outputList;
private List<JudgeCase> judgeCaseList;
private Question question;
private QuestionSubmit questionSubmit;
}
|
- 定义判题策略接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public interface JudgeStrategy {
JudgeInfo doJudge(JudgeContext judgeContext);
}
|
- 实现默认判题策略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
| package com.wl2o2o.smartoj.judge.strategy;
import cn.hutool.json.JSONUtil;
import com.wl2o2o.smartoj.model.dto.question.JudgeCase;
import com.wl2o2o.smartoj.model.dto.question.JudgeConfig;
import com.wl2o2o.smartoj.model.dto.questionsubmit.JudgeInfo;
import com.wl2o2o.smartoj.model.entity.Question;
import com.wl2o2o.smartoj.model.enums.JudgeInfoMessageEnum;
import java.util.List;
public class DefaultJudgeStrategy implements JudgeStrategy {
@Override
public JudgeInfo doJudge(JudgeContext judgeContext) {
JudgeInfo judgeInfo = judgeContext.getJudgeInfo();
Long memory = judgeInfo.getMemory();
Long time = judgeInfo.getTime();
List<String> inputList = judgeContext.getInputList();
List<String> outputList = judgeContext.getOutputList();
Question question = judgeContext.getQuestion();
List<JudgeCase> judgeCaseList = judgeContext.getJudgeCaseList();
JudgeInfoMessageEnum judgeInfoMessageEnum = JudgeInfoMessageEnum.ACCEPTED;
JudgeInfo judgeInfoResponse = new JudgeInfo();
judgeInfoResponse.setMemory(memory);
judgeInfoResponse.setTime(time);
if (outputList.size() != inputList.size()) {
judgeInfoMessageEnum = JudgeInfoMessageEnum.WRONG_ANSWER;
judgeInfoResponse.setMessage(judgeInfoMessageEnum.getValue());
return judgeInfoResponse;
}
for (int i = 0; i < judgeCaseList.size(); i++) {
JudgeCase judgeCase = judgeCaseList.get(i);
if (!judgeCase.getOutput().equals(outputList.get(i))) {
judgeInfoMessageEnum = JudgeInfoMessageEnum.WRONG_ANSWER;
judgeInfoResponse.setMessage(judgeInfoMessageEnum.getValue());
return judgeInfoResponse;
}
}
String judgeConfigStr = question.getJudgeConfig();
JudgeConfig judgeConfig = JSONUtil.toBean(judgeConfigStr, JudgeConfig.class);
Long needMemoryLimit = judgeConfig.getMemoryLimit();
Long needTimeLimit = judgeConfig.getTimeLimit();
if (memory > needMemoryLimit) {
judgeInfoMessageEnum = JudgeInfoMessageEnum.MEMORY_LIMIT_EXCEEDED;
judgeInfoResponse.setMessage(judgeInfoMessageEnum.getValue());
return judgeInfoResponse;
}
if (time > needTimeLimit) {
judgeInfoMessageEnum = JudgeInfoMessageEnum.TIME_LIMIT_EXCEEDED;
judgeInfoResponse.setMessage(judgeInfoMessageEnum.getValue());
return judgeInfoResponse;
}
judgeInfoResponse.setMessage(judgeInfoMessageEnum.getValue());
return judgeInfoResponse;
}
}
|
- 新增一种判题策略,在
JudgeServiceImpl中通过if else的方式来选择使用哪种策略
1
2
3
4
5
| JudgeStrategy judgeStrategy = new DefaultJudgeStrategy();
if (language.equals("java")) {
judgeStrategy = new JavaLanguageJudgeStrategy();
}
JudgeInfo judgeInfo = judgeStrategy.doJudge(judgeContext);
|
注意:如果判题策略的过程比较复杂,service 实现类代码会比较臃肿。
那么为了让调用方写更少的代码、调用最简单化。
我们可以将判断使用哪个策略的部分代码抽离出来,编写StrategyManage类,用来单独判断策略。
- 编写
StrategyManage类,用来单独判断策略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
@Service
public class JudgeManager {
JudgeInfo doJudge(JudgeContext judgeContext) {
QuestionSubmit questionSubmit = judgeContext.getQuestionSubmit();
String language = questionSubmit.getLanguage();
JudgeStrategy judgeStrategy = new DefaultJudgeStrategy();
if ("java".equals(language)) {
judgeStrategy = new JavaLanguageJudgeStrategy();
}
return judgeStrategy.doJudge(judgeContext);
}
}
|
🆗,完成!
知识点 - 设计模式:
- 工厂模式
可配置化
- 代理模式

- 策略模式
我的理解:抽离方法,解耦思想
代码沙箱的实现
什么是代码沙箱:
为了解耦并将代码沙箱单独作为一个服务/接口来调用,将判题逻辑分为判题模块与代码沙箱两个模块。
代码沙箱只负责接收代码的输入与输入用例,只返回编译运行的结果,不负责判题,判题逻辑单独交给判题模块负责。
下面以Java语言为例,实现代码沙箱
TODO: 扩展其他语言的实现
根据我们的架构来看,我们的代码沙箱最终需要提供一个接口来进行调用
新建Spring Boot Web项目(JDK8/Boot 2.7)
编写测试接口,测试能否访问
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| package com.wl2o2o.smartojcodesandbox.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController("/")
public class MainController {
@GetMapping("/health")
public String healthCheck() {
return "ok";
}
}
|
Java 原生实现代码沙箱
原生就是不借助于任何的第三方库,用最干净的方式实现代码沙箱
逻辑:
接收代码 =javac=> 编译代码 =java=> 执行代码
因为一般来说OJ系统中一般都对于用户的输入有相关要求,所以为了更方便处理,我们把类名统一写成Main,减少类名不一致的风险。(关键是还不用从用户输入的代码中去提取类名)
示例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
System.out.println("结果:" + (a + b));
}
}
|
编译执行代码:
1
2
| javac -encoding utf8 .\Main.java
java -cp . Main 1 2
|
核心流程实现
核心实现思路:用程序来代替人工,用程序操作命令行,去编译代码
关键类:Java进程执行管理类
- 把用户文件保存为文件
- 编译代码,得到 class 文件
- 执行代码,得到输出结果
- 从控制台,收集整理输出结果
- 文件清理
- 错误处理,提升程序健壮性
把用户文件保存为文件
- 引入
hutool工具类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.8.8</version>
</dependency>
|
- 新建UUID随机目录,每个用户的代码都存放于一个独立的文件夹中,便于维护
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String globalPathName = userDir + File.separator + GLOBAL_CODE_DIR_NAME;
if (!FileUtil.exist(globalPathName)) {
FileUtil.mkdir(globalPathName);
}
String userCodeParentPathName = globalPathName + File.separator + UUID.randomUUID();
String userCodePath = userCodeParentPathName + File.separator + GLOBAL_JAVA_CLASS_NAME;
File file = FileUtil.writeString(code, userCodePath, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
|
口诀:一般情况下,程序会向输入流里写,会从输出流中读取 ————其实取决于进程
执行程序
- 编译代码,得到 class 文件
如何解决运行结果乱码:
java -Dfile.encoding=utf8 -cp %s Main %s
如果需要交互式(ACM),需要和用户交互的方式,让用户不断输入内容以获得输出
对于此类程序,我们需要使用OutPutStream向程序释放资源,流关闭终端发送参数,并及时获取结果,最后要
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
public static ExecuteMessage runInterProcessAndGetMessage(Process runProcess, String opName, String args) {
ExecuteMessage executeMessage = new ExecuteMessage();
try {
OutputStream outputStream = runProcess.getOutputStream();
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream);
String[] split = args.split(" ");
outputStreamWriter.write(StrUtil.join("\n", (Object) split) + "\n");
outputStreamWriter.flush();
int exitValue = runProcess.waitFor();
executeMessage.setExitValue(exitValue);
InputStream inputStream = runProcess.getInputStream();
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
StringBuilder compileOutputStringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
String output;
while ((output = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null ) {
compileOutputStringBuilder.append(output);
}
executeMessage.setMessgae(compileOutputStringBuilder.toString());
outputStream.close();
outputStreamWriter.close();
inputStream.close();
runProcess.destroy();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return executeMessage;
}
}
|
异常情况演示
执行阻塞,占用资源
占用内存,不释放
读文件,文件信息泄露
写文件,越权植入木马
运行其他程序
执行高危命令
怎么解决?
- 超时控制
- 限制给用户分配的资源
- 限制代码,黑白名单
- 限制用户的操作权限,(文件、网络、执行)
- 运行环境隔离
a. 超时控制
怎么显示执行时间?创建一个新的线程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(SLEEP_TIME);
System.out.println("超时了,中断!");
runProcess.destroy();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}).start();
|
b. 限制给用户分配的资源
怎么限制呢?一个最简单的办法:通过JVM自带的一个堆内存限制参数:-Xmx256m
1
| java -Xmx256m -Dfile.encoding=utf8 -cp %s Main %s
|
但是我们要注意!!!-Xmx参数,Java的堆内存限制,并不完全等同于系统占用的资源,可能会超出
面试重点:
JVM层面的内存限制安全吗?
答:并不安全,若要进行严格的内存控制,我们需要在内存方面进行进一步的限制
如果是在Linux 系统的话,我们可以使用 cgrop 来实现对某一个进程的 CPU 或者内存资源的分配
使用方法:
c. 限制代码,黑白名单
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| private static final List<String> blacklist = Arrays.asList("File", "exec");
private static final WordTree WORD_TREE;
static {
WORD_TREE = new WordTree();
WORD_TREE.addWords(blacklist);
}
@Override
public ExecuteCodeResponse executeCode(ExecuteCodeRequest executeCodeRequest) {
List<String> inputList = executeCodeRequest.getInputList();
String code = executeCodeRequest.getCode();
String language = executeCodeRequest.getLanguage();
FoundWord foundWord = WORD_TREE.matchWord(code);
if (foundWord != null) {
System.out.println("包含禁止词汇:" + foundWord.getFoundWord());
return null;
}
···
}
}
|
d. 限制用户的操作权限
限制用户对文件、内存、CPU、网络等资源的访问。
Java安全管理器(Security Manager),是Java提供的可以保护JVM、Java安全的机制,可以实现更加严格的控制。
编写默认的安全管理器,只需继承Java自带的SecurityManager
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| package com.wl2o2o.smartojcodesandbox.security;
import java.security.Permission;
public class DefaultSecurityManager extends SecurityManager {
@Override
public void checkPermission(Permission perm) {
throw new SecurityException(perm.getActions() + "权限被禁用!");
}
}
|
e. 实现其他权限控制
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| package com.wl2o2o.smartojcodesandbox.security;
import java.security.Permission;
public class MySecurityManager extends SecurityManager {
@Override
public void checkPermission(Permission perm) {
System.out.println(perm);
}
@Override
public void checkExec(String cmd) {
throw new SecurityException("exec 权限被禁用!" + cmd);
}
@Override
public void checkRead(String file) {
}
@Override
public void checkWrite(String file) {
}
@Override
public void checkDelete(String file) {
}
@Override
public void checkConnect(String host, int port) {
}
}
System.setSecurityManager(new MySecurityManager());
|
实际上,我们只需要对涉及到相关执行命令的子程序进行安全管理,所以采用如下步骤进行配置(也就是配置一个安全管理类加载路径—— **;%s -Djava.security.manager=%s", SECURITY_MANAGER_PATH, SECURITY_MANAGER_CLASS_NAME**)
步骤:
- 编写安全管理器
- 编译成class文件
- 去掉包名
- 放置在
**resources**目录之下 - 指定
**final**变量,存放管理器class名以及路径 - 完成类加载路径配置:
1
2
| String runCmd = String.format("java -Xmx256m -Dfile.encoding=utf8 -cp %s;%s -Djava.security.manager=%s Main %s", userCodeParentPath, SECURITY_MANAGER_PATH, SECURITY_MANAGER_CLASS_NAME, input);
Process runProcess = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(runCmd);
|
这样就可以实现直接在子程序中直接运用安全管理器。
但是,安全管理器还是存在不足的地方,比如:
优点:
权限控制很灵活,实现简单
缺点:
- 如果要做比较严格的安全校验,需要判断哪些文件允许读写,粒度太细,难以精细化控制
- 安全管理器本身都是Java代码,难免存在漏洞(等于说还是程序上的控制,不属于系统层面上的)
- 而且不推荐 Java8 以上版本使用
f. 运行环境隔离
系统层面上,把用户程序封装到沙箱里,和宿主机(我们的电脑/服务器)隔离开
怎么实现:(两种方案)
- Docker 容器技术可以实现(底层是 cgroup 和 namespace 等方式实现)
- cgroup
注意:其实完全使用 Docker 的话,也很难实现绝对安全控制,可以结合 Java 安全管理器进行使用
前端项目初始化
环境
nodejs版本:v18.16.0 或者v16
npm版本:v9.5.1
初始化
安装vue-cli脚手架初始化工具
npm install -g @vue/cli
先确认是否安装成功:
vue -V(V是大写)
如果找不到命令,建议重装npm,重新配置环境变量
创建项目
vue create + 项目名
vue create smartoj-frontend

运行项目
是否成功?引入组件进行测试 :重装或者解决问题
前端工程化配置
因为脚手架生成项目的时候,已经勾选代码格式校验,以及美化插件,所以需要在IDE手动开启,避免与IDE的格式化冲突。格式化命令:Ctrl + Shift + L


更改项目的布局
引入组件
安装arco.design组件库:https://arco.design/vue/docs/start
快速上手:
a. 安装
1
2
3
4
|
npm install --save-dev @arco-design/web-vue
yarn add --dev @arco-design/web-vue
|
b. 完整引入
项目通用布局
- 新建一个BasicLayout布局,在app.vue中引入
1
2
3
| <div id="app">
<BasicLayout />
</div>
|
并设置好布局样式
- 通用菜单GloableHeader布局
目标:可根据路由配置信息动态生成菜单内容。实现更通用更自动的菜单配置。
实现步骤:
- 提取通用路由文件
- 菜单组件读取路由,动态渲染菜单项
- 绑定跳转事件(为什么?因为通过v-for可以实现router路由的同步,但是不能够实现路径的跳转)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| <a-menu
mode="horizontal"
theme="dark"
:default-selected-keys="['1']"
@menu-item-click="doMenuClick"
>
...
<a-menu-item v-for="item in routes" :key="item.path">
{{ item.name }}
</a-menu-item>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { routes } from "@/router/routes";
import { useRouter } from "vue-router";
const router = useRouter();
const doMenuClick = (key: string) => {
router.push({
path: key,
});
};
</script>
|
- 此时刷新的话,不会记录路由的状态,所以这一步我们实现:同步路由的更新到菜单项高亮(点击–>触发点击事件,跳转更新–>同步菜单栏高亮)
实现方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| const router = useRouter();
const selectedKeys = ref(["/"]);
router.afterEach((to, from, failure) => {
selectedKeys.value = [to.path];
});
|
逻辑:首先点击菜单栏 => 跳转更新路由 => 更新路由之后,同步高亮状态
全局状态管理
todo 看官方文档!!!!!!!!!!
用到了一个 vuex 库,另外还有 pinia 库可用于全局状态管理
todo 再了解一下https://blog.51cto.com/u_15961676/6148140
所有页面共享全局的变量,而不是局限于某一个页面。
已登陆的用户信息(每一个页面几乎都要用)
提供了一套增删改查的全局变量 API,只不过多了一些功能,比如说时间旅行

可以直接参考购物车示例:链接
state:存储的状态信息,比如用户信息
mutation(尽量同步):定义了对变量进行增删改查的方法
actions(支持异步):执行异步操作,并且触发 mutation 的更改
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| import shop from '../../api/shop'
// initial state
const state = () => ({
loginUser: {
}
})
// getters
const getters = {}
// actions
const actions = {
async getAllProducts ({ commit }) {
const products = await shop.getProducts()
commit('setProducts', products)
}
}
// mutations
const mutations = {
setProducts (state, products) {
state.all = products
},
decrementProductInventory (state, { id }) {
const product = state.all.find(product => product.id === id)
product.inventory--
}
}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
getters,
actions,
mutations
}
|
获取状态变量:
1
2
| const store = useStore();
store.state.user?.loginUser
|
修改状态变量:
1
2
3
| store.dispath("user/getLoginUser", {
userNama: "CSGUIDER",
})
|
权限管理
就是用一套通用的机制,去定义哪个页面需要什么权限。
思路:
- 在 router 路由文件中,对每个需要权限的路由进行配置;
- 在全局路由头文件中,绑定一个全局路由监听。每次访问页面时,获取用户需要访问的路由信息,进行判断访问权限。
- 有权限? 跳转 : 拦截或者跳转401鉴权或者登录页
小尾巴:
- 单独定义一个文件,控制路由文件的显隐
- 完善模板。
优化页面布局
- 底部footer布局优化
- 用户名换行问题
- 导航栏间距优化,content区域优化padding布局
根据权限隐藏菜单路由
思路:
- 通过v-for循环来判断item中的meta中是否含有hideInMenu(效率低,而且不能与v-if连用)
- 定义一个visibleRouter函数来过滤路由
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<a-menu-item v-for="item in visibleRoutes" :key="item.path">
{{ item.name }}
</a-menu-item>
const visibleRoutes = routes.filter((item, index) => {
if (item.meta?.hideInMenu) {
return false;
}
return true;
});
|
加上判断用户权限的逻辑
记录一个小bug,没搞懂,可能与computed有关
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| const store = useStore();
const visibleRoutes = computed(() => {
return routes.filter((item, index) => {
if (item.meta?.hideInMenu) {
return false;
}
if (!checkAcess(store.state.user.loginUser, item?.meta?.access as string)) {
return false;
}
return true;
});
});
|
注意,这里使用计算属性,是为了当登录用户信息发生变更时,出发菜单栏的重新渲染,显示符合权限的菜单栏
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
const router = useRouter();
const store = useStore();
const visibleRoutes = computed(() => {
return routes.filter((item, index) => {
if (item.meta?.hideInMenu) {
return false;
}
if (!checkAcess(store.state.user.loginUser, item?.meta?.access as string)) {
return false;
}
return true;
});
});
|
全局项目入口
预留一个可以编辑全局初始化逻辑的代码,可以藏一个佛祖哈哈哈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
const doInit = () => {
console.log("hello 欢迎来到我的项目");
};
onMounted(() => {
doInit();
});
|
前后端联调
1 安装请求工具类 Axios
官方文档:
https://axios-http.com/docs/intro
代码:
npm install axios
2 编写调用后端的代码
传统情况下,每个请求都要单独编写代码。至少得写一个请求路径
完全不用!!!我们可以完全借助 openai 的 oneApi 插件来一键生成我们的后端请求代码。
官方文档:
https://github.com/ferdikoomen/openapi-typescript-codegen
代码:
npm install openapi-typescript-codegen --save-dev
根据接口文档来生成前端请求代码:
openapi --input [http://localhost:8101/api/v2/api-docs](http://localhost:8121/api/v2/api-docs) --output ./generated --client axios
用户登录功能
自动登录
- 编写获取远程用户登陆信息的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| actions: {
async getLoginUser({ commit, state }, payload) {
const res = await UserControllerService.getLoginUserUsingGet();
if (res.code === 0) {
commit("updateUser", res.data);
} else {
commit("updateUser", {
...state.loginUser,
userRole: ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN,
});
}
commit("updateUser", payload);
},
},
|
- 去哪里触发 getLoginUser 函数的执行?肯定是在一个全局位置
例如:
1) 路由选择
2) 全局页面入口
3) 全局通用布局
这里我们选择第一种方案,可以直接在全局权限管理的路由拦截中判断用户是否已经登陆
全局权限管理优化
- 新建 access/index.ts 文件,把愿原来的路由拦截、权限校验的逻辑放在独立的文件中。
优势:只要不引入到 main.ts 中,就不会开启,不会对项目有影响
- 调用后端接口,编写权限管理和自动登录的逻辑
如果没有登录过,那就自动登录:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| const loginUser = store.state.user.loginUser;
if (!loginUser || !loginUser.userRole) {
await store.dispatch("user/getLoginUser");
}
|
完整代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| import router from "@/router";
import store from "@/store";
import ACCESS_ENUM from "@/access/accessEnum";
import checkAccess from "@/access/checkAccess";
router.beforeEach(async (to, from, next) => {
console.log("登陆用户信息", store.state.user.loginUser);
const loginUser = store.state.user.loginUser;
if (!loginUser || !loginUser.userRole) {
await store.dispatch("user/getLoginUser");
}
const needAccess = (to.meta?.access as string) ?? ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN;
if (needAccess !== ACCESS_ENUM.NOT_LOGIN) {
if (!loginUser || !loginUser.userRole) {
next(`/user/login?redirect=${to.fullPath}`);
return;
}
if (!checkAccess(loginUser, needAccess)) {
next("/noAuth");
return;
}
}
next();
});
|
支持多套布局与用户登录注册功能开发
- 在 routes 路由文件中新建一套用户路由,使用 vue-router 自带的子路由机制,实现布局和嵌套路由,然后隐藏路由即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| export const routes: Array<RouteRecordRaw> = [
{
path: "/user",
name: "用户",
component: UserLayout,
children: [
{
path: "/user/login",
name: "用户登录",
component: UserLoginView,
},
{
path: "/user/register",
name: "用户注册",
component: UserRegisterView,
},
],
},
]
|
- 新建 UserLayout、UserLoginView、UserRegisterView 页面,并且在 routes 中引入
编写登录界面、以及登录逻辑,为了方便,直接复用我们写好的获取登陆用户的代码,后期也可以通过优化来,直接获取登录用户,然后塞给我们的前端界面。
TODO:编写用户注册页面
- 因为我们在 app.vue 中全局引入了 GloableHeader,因此需要借助 v-if 来实现用户布局中不显示全局头,使用户界面更加美观
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <template v-if="route.path.startsWith('/user')">
<router-view />
</template>
<template v-else>
<BasicLayout />
</template>
|
TODO:这种方式可定不是最优雅的,最理想的情况下是直接读取 routes.ts,在这个文件中自定义多套布局,然后自动使用页面布局。
Tips:嵌套路由子菜单
- 登录页面开发
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| <a-form
style="max-width: 480px; margin: 0 auto"
label-align="left"
auto-label-width
:model="form"
@submit="handleSubmit"
>
<a-form-item field="userAccount" label="账号">
<a-input v-model="form.userAccount" placeholder="请输入账号" />
</a-form-item>
<a-form-item field="userPassword" tooltip="密码不少于 8 位" label="密码">
<a-input-password
v-model="form.userPassword"
placeholder="请输入密码"
/>
</a-form-item>
<a-form-item>
<a-button type="primary" html-type="submit" style="width: 120px"
>登录</a-button
>
</a-form-item>
</a-form>
|
- 尝试登录逻辑,发现还是获取不到用户登陆的信息

TODO:为什么要打开携带 Cookie?不携带 cookie 就相当于前后端无关联。
本次页面开发计划
完善:
- 用户注册页面
- 用户个人信息页
计划:
- 创建题目界面
- 题目管理界面(Admin)
- 题目列表页(主页展示、判题状态展示)
- 在线做题页
- 题目提交列表页
- 题目提交统计页
组件技术选型
首先技术选型,先接入组件查看是否有冲突
组件:
- md 编辑器(字节的 bytemd —— https://github.com/bytedance/bytemd)
- 代码编辑器(微软的 monaco Editor —— https://github.com/microsoft/monaco-editor)
官方整合教程:https://github.com/microsoft/monaco-editor/blob/main/docs/integrate-esm.md
MD 编辑器:
- 引入 MD 编辑器:
1
2
| npm i @bytemd/vue-next
npm i @bytemd/plugin-highlight @bytemd/plugin-gfm
|
- 新建 MdEditor 组件,编写代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| <template>
<Editor :value="value" :plugins="plugins" @change="handleChange" />
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import gfm from "@bytemd/plugin-gfm";
import highlight from "@bytemd/plugin-highlight";
import { Editor, Viewer } from "@bytemd/vue-next";
import { ref } from "vue";
const plugins = [
gfm(),
highlight(),
// Add more plugins here
];
const value = ref("");
const handleChange = (v: string) => {
value.value = v;
};
</script>
<style scoped></style>
|
- 美化样式
代码编辑器的右上角带有一个 byteMd GitHub图标广告,我们可以通过样式来去掉:
1
2
3
| .bytemd-toolbar-icon.bytemd-tippy.bytemd-tippy-right:last-child {
display: none;
}
|
编辑器引入成功,但是我们输入的值,目前还不能被监听到,也就是还不能取出来,所以,我们需要通过定义一个组件来实现把输入的值暴漏给父组件,便于父组件去使用,同时也是提高 md 编辑器的通用性、复用性
- 怎么得到组件内的值?(组件自定义事件?)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| /**
* 定义组件属性类型
*/
interface Props {
value: string;
handleChange: (v: string) => void;
}
/**
* 给组件指定初始值
*/
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<Props>(), {
value: () => "",
handleChange: (v: string) => {
console.log(v);
},
});
|
代码编辑器:
- 安装编辑器
1
| npm install monaco-editor
|
- vue-cli项目(webpack项目)整合monaco-editor
1
| npm install monaco-editor-webpack-plugin
|
- 在 vue.config.js 中配置webpack插件:
全量加载或者按需加载:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| const { defineConfig } = require("@vue/cli-service");
const MonacoWebpackPlugin = require("monaco-editor-webpack-plugin");
module.exports = defineConfig({
transpileDependencies: true,
chainWebpack(config) {
config.plugin("monaco").use(new MonacoWebpackPlugin());
},
});
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| const MonacoWebpackPlugin = require('monaco-editor-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
chainWebpack: config => {
config.plugin('monaco-editor').use(MonacoWebpackPlugin, [
{
languages: ['json', 'go', 'css', 'html', 'java', 'javascript', 'less', 'markdown', 'mysql', 'php', 'python', 'scss', 'shell', 'redis', 'sql', 'typescript', 'xml'],
features: ['format', 'find', 'contextmenu', 'gotoError', 'gotoLine', 'gotoSymbol', 'hover' , 'documentSymbols']
}
])
}
}
|
- 整合教程
如何使用 Monaco Editor ?查看示例教程:
https://microsoft.github.io/monaco-editor/playground.html?source=v0.40.0#example-creating-the-editor-hello-world
整合教程参考:
http://chart.zhenglinglu.cn/pages/2244bd/#%E5%9C%A8-vue-%E4%B8%AD%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8
注意,monaco editor在读写值的时候,要使用toRaw(编辑器实例)的语法来执行操
作,否则会卡死。
示例整合代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| <template>
<div id="code-editor" ref="codeEditorRef" style="min-height: 400px" />
{{ value }}
<a-button @click="fillValue">填充值</a-button>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import * as monaco from "monaco-editor";
import { onMounted, ref, toRaw } from "vue";
const codeEditorRef = ref();
const codeEditor = ref();
const value = ref("hello world");
const fillValue = () => {
if (!codeEditor.value) {
return;
}
// 改变值
toRaw(codeEditor.value).setValue("新的值");
};
onMounted(() => {
if (!codeEditorRef.value) {
return;
}
// Hover on each property to see its docs!
codeEditor.value = monaco.editor.create(codeEditorRef.value, {
value: value.value,
language: "java",
automaticLayout: true,
colorDecorators: true,
minimap: {
enabled: true,
},
readOnly: false,
theme: "vs-dark",
// lineNumbers: "off",
// roundedSelection: false,
// scrollBeyondLastLine: false,
});
// 编辑 监听内容变化
codeEditor.value.onDidChangeModelContent(() => {
console.log("目前内容为:", toRaw(codeEditor.value).getValue());
});
});
</script>
<style scoped></style>
|
- 暴漏内容给父组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| /**
* 定义组件属性类型
*/
interface Props {
value: string;
handleChange: (v: string) => void;
}
/**
* 给组件指定初始值
*/
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<Props>(), {
value: () => "",
handleChange: (v: string) => {
console.log(v);
},
});
|
todo: 扩展:用diff editor对比用户代码和标准答案的区别
页面开发
创建题目界面
小技巧:
自定义代码模板:
在JetBrains系列编辑器中打开设置,搜索live Templates,先创建一个自定义模板组,在组下创建代码模板。
效果:输入缩写,即可生成模板代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <template>
<div id="$ID$"></div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
$END$
</script>
<style scoped>
#$ID$ {
}
</style>
|

- 利用 oneapi 根据后端接口文档,生成前端请求代码
需要注意的是,每次生成请求代码,需要配置一下携带 cookie
1
| openapi --input http://localhost:8121/api/v2/api-docs --output ./generated --client axios
|
- 使用表单组件
示例代码:https://arco.design/vue/component/form
此处我们用到了
注意,我们自定义的代码编辑器组件不会被组件库识别,需要手动指定vlue和handleChange函数。
题目管理界面
- 使用表格组件,找到自定义操作的示例:https://arco.design/vue/component/table#custom
- 查询数据
- 定以表格列
- 加载数据
- 调整格式
JSON 数据的处理方法:
1) 使用组件库的自带语法,自动格式化(方便)
2) 像定义 optional 操作按钮一样,自定义渲染(灵活)
- 添加、删除、更新操作
删除之后要执行 loadData 刷新数据
如果想学 React Ant Design 框架的管理页面的开发,看用户中心的项目
更新页面的开发
因为更新与创建题目都是相同的操作,所以直接复用即可。
复用的关键:怎么区分两个页面?
1) 定义不用的路由
2) 对于不用题目加上题目 id 的请求参数
3) 更新页需要多一步显示之前信息的操作,最后还需要更改后端的请求接口
计划完成
小计划:
- 解决分页题目信息不跳转 Bug ,以及管理页面刷新之后需要重新登录的 Bug
- 题目列表搜索页面开发
- 题目浏览页面(做题)开发(左侧题目信息,右侧代码编辑器,对标 Leetcode)
后端:
- 判题机和代码沙箱
简历完善点
实际运行上述程序时,我们会发现,内存占用到达一定空间后,程序就自动报错:java.lang.OutOfMemoryError:Java heap space,而不是无限增加内存占用,直到系统死机。这是JVM的一个保护机制。
- 内存使用情况,可以使用JVisualVM或JConsole工具,连接到JVM虚拟机上来可视化查看运行状态。(使用过相关工具)
- 数据结构相关的知识点:HuTool的
WordTree字典树工具,他可以使用更少的空间存储更多的词汇, 实现更加便捷的查找。 - Java安全管理器和 Docker 相结合(需要再进行详细了解一下)
TODO
详细了解一下糊涂工具类
Java安全管理器











